Skorokhod's embedding theorem
In mathematics and probability theory, Skorokhod's embedding theorem is either or both of two theorems that allow one to regard any suitable collection of random variables as a Wiener process (Brownian motion) evaluated at a collection of stopping times. Both results are named for the Ukrainian mathematician A.V. Skorokhod.
Skorokhod's first embedding theorem
Let X be a real-valued random variable with expected value 0 and finite variance; let W denote a canonical real-valued Wiener process. Then there is a stopping time (with respect to the natural filtration of W), τ, such that Wτ has the same distribution as X,
and
Skorokhod's second embedding theorem
Let X1, X2, ... be a sequence of independent and identically distributed random variables, each with expected value 0 and finite variance, and let
Then there is a non-decreasing (a.k.a. weakly increasing) sequence τ1, τ2, ... of stopping times such that the 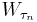 have the same joint distributions as the partial sums Sn and τ1, τ2 − τ1, τ3 − τ2, ... are independent and identically distributed random variables satisfying
have the same joint distributions as the partial sums Sn and τ1, τ2 − τ1, τ3 − τ2, ... are independent and identically distributed random variables satisfying
and
References
- Billingsley, Patrick (1995). Probability and Measure. New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.. ISBN 0-471-00710-2. (Theorems 37.6, 37.7)
![\mathbb{E}[\tau] = \mathbb{E}[X^{2}]](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/efff0a1353ac9167f44e1da0a4d3fd0e.png)
![\mathbb{E}[\tau^{2}] \leq 4 \mathbb{E}[X^{4}].](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/751e91b63c2cb938b80d3f16a889e9c3.png)
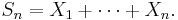
![\mathbb{E}[\tau_{n} - \tau_{n - 1}] = \mathbb{E}[X_{1}^{2}]](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/08f09e73c3442914fed9c0ad122516df.png)
![\mathbb{E}[(\tau_{n} - \tau_{n - 1})^{2}] \leq 4 \mathbb{E}[X_{1}^{4}].](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/ad46d115e00625cc59fabe2b6ab1a5de.png)